Lupus erythematosus, often simply referred to as lupus, is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body. This article aims to shed light on the symptoms and treatment options associated with this complex condition.
Symptoms of Lupus Erythematosus:
- Fatigue: Lupus commonly presents with persistent fatigue, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Painful and swollen joints are hallmark symptoms of lupus, often resembling arthritis. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
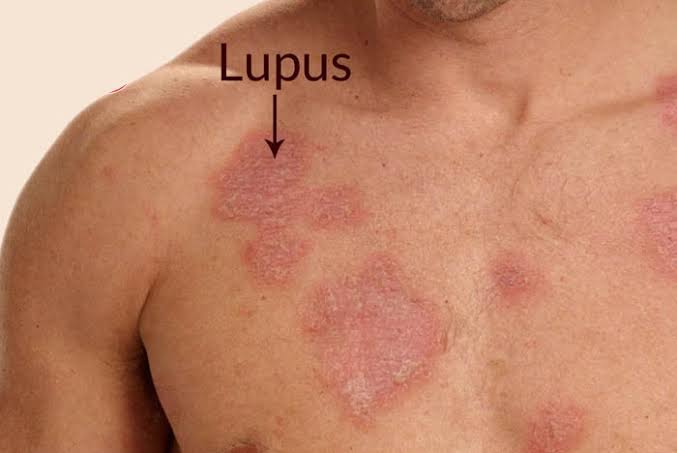
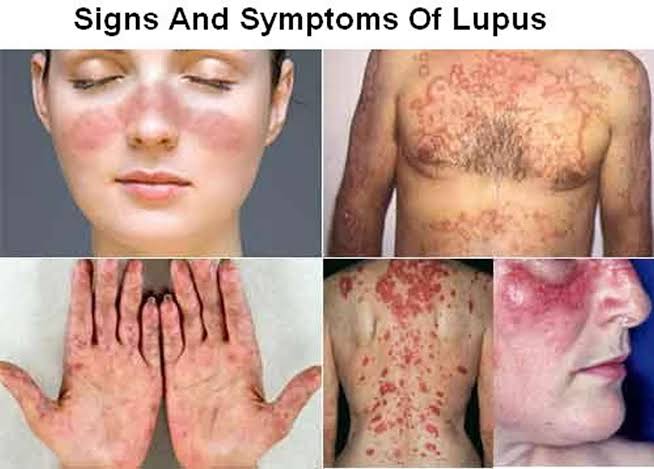
- Skin Rashes: Lupus often manifests on the skin, causing a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose. Other skin issues may include sensitivity to sunlight and the development of lesions.
- Fever: Unexplained fever is a frequent symptom of lupus, signaling inflammation and an overactive immune system.
- Photosensitivity: Individuals with lupus may experience heightened sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in rashes and other skin reactions.
- Kidney Involvement: Lupus nephritis can occur, leading to kidney inflammation and potential damage. This may manifest as changes in urination patterns and swelling.
- Chest Pain: Lupus can affect the heart and lungs, causing chest pain and discomfort. Inflammation may lead to complications like pleurisy.
- Hair Loss: Some individuals with lupus may experience hair loss, which can be distressing and affect self-esteem.
Diagnosis and Types:
Diagnosing lupus can be challenging, as its symptoms mimic those of other conditions. Doctors often use a combination of physical examinations, medical history, blood tests, and imaging studies to reach a conclusive diagnosis. There are various types of lupus, with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) being the most common and affecting multiple organ systems.
Treatment Options:
- Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): For managing pain and inflammation.
- Antimalarial Drugs: Such as hydroxychloroquine, which can help control symptoms.
- Corticosteroids: Prescribed for severe symptoms and flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs like methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil are used to suppress the immune system’s activity, preventing it from attacking healthy tissues.
- Biologics: In certain cases, biologic drugs like belimumab may be prescribed to specifically target components of the immune system involved in lupus.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure.
- Regular exercise to manage joint pain and fatigue.
- Adequate rest and stress management.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor symptoms, adjust treatment plans, and address emerging concerns promptly.
Conclusion
Living with lupus requires ongoing management and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals. While there is no cure, advancements in medical research continue to enhance our understanding of lupus and improve treatment options. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are vital in helping individuals with lupus lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this autoimmune condition.








[…] RELATED:Lupus Erthematosus – Chronic Autoimmune disease […]