Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is a condition where a woman’s ovaries produce an abnormal amount of androgens, which are sometimes referred to as “male hormones,” although women naturally produce them as well, just in smaller amounts. These elevated androgen levels can interfere with the normal function of the ovaries, leading to a variety of symptoms.
PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility in women, affecting approximately 1 in 10 women globally. Although the exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, it is believed that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of the condition. The condition can also lead to long-term health issues such as diabetes, heart disease, and endometrial cancer if not properly managed.
PCOS Symptoms: How to Recognize the Condition
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from woman to woman by Trusted Source. Some women experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe effects. Here are some common symptoms that women with PCOS may experience:
- Irregular Periods: One of the most common signs of PCOS is irregular menstruation. Women with PCOS often have infrequent, prolonged, or absent periods. This happens because the hormonal imbalance affects the normal process of ovulation.
- Excess Hair Growth: Women with PCOS may experience hirsutism, which is excessive hair growth on the face, chest, abdomen, or back. This occurs due to the elevated levels of male hormones in the body.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Increased androgen levels can also cause acne and oily skin, which is often more severe than typical teenage acne.
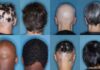
- Thinning Hair on the Scalp: Some women with PCOS may notice thinning hair or hair loss, often along the front or sides of the scalp.
- Weight Gain: PCOS can lead to weight gain or difficulty losing weight. Women with PCOS tend to have a higher risk of obesity, which may further complicate managing the condition.
- Infertility: PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility because it can interfere with the release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation). Many women with PCOS find it difficult to get pregnant without medical intervention.
The Causes of PCOS: What You Need to Know
While the exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Imbalance: As mentioned, women with PCOS have an excess of male hormones (androgens). This hormonal imbalance disrupts the normal ovarian function and leads to irregular ovulation and periods.
- Genetics: PCOS tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. If your mother or sister has PCOS, you may be more likely to develop the condition as well.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS also have insulin resistance, which means the body’s cells do not respond to insulin properly. This leads to higher insulin levels in the blood, which can increase androgen production and worsen symptoms like weight gain and acne.
- Inflammation: Higher levels of inflammation have been linked to PCOS. Chronic inflammation can worsen insulin resistance and affect the overall health of the ovaries.
Although the exact mechanism behind PCOS is complex, understanding these factors can help guide treatment options and lifestyle changes to manage the condition effectively.
How to Manage PCOS: Treatment and Lifestyle Changes
There is no cure for PCOS, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, the symptoms can be effectively managed. Here are some key strategies for managing PCOS:
1. Healthy Diet and Nutrition
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet is crucial for managing PCOS. Certain foods can help regulate hormones and reduce symptoms like weight gain and insulin resistance. Here are some dietary tips for women with PCOS:
- Eat Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods that have a low glycemic index (GI) help regulate blood sugar and insulin levels. These include whole grains, vegetables, legumes, and fruits like berries.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate insulin levels and improve digestion.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats like those found in avocados, olive oil, and nuts to support hormone regulation and overall health.
- Limit Processed Sugars and Carbs: Avoid foods high in refined sugars and carbohydrates, such as sugary snacks, soda, and white bread. These can spike insulin levels and worsen PCOS symptoms.
Consulting with a registered dietitian who specializes in PCOS can help create a meal plan tailored to your specific needs.
2. Regular Exercise
Exercise is essential for managing PCOS, as it helps regulate blood sugar, reduce insulin resistance, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, cycling, swimming, and strength training are beneficial for improving insulin sensitivity and overall health.
3. Medications for Hormonal Imbalance
Several medications can help manage the hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS:
- Birth Control Pills: Oral contraceptives can regulate periods, reduce excess hair growth, and help manage acne by balancing hormones.
- Metformin: This medication is used to manage insulin resistance. It helps improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which can aid in weight loss and reduce symptoms of PCOS.
- Anti-androgen Medications: These medications, such as spironolactone, can help reduce excess hair growth and acne by blocking the effects of male hormones.
Consulting with your healthcare provider is essential to find the right treatment plan for you.
4. Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate PCOS symptoms by increasing hormone imbalances. Practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve overall health.
5. Consider Fertility Treatment
For women with PCOS who are struggling with infertility, treatments such as ovulation induction medications (Clomid) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help improve the chances of pregnancy. Consult a fertility specialist for personalized advice and treatment options.
Conclusion: Living with PCOS
Although PCOS is a lifelong condition, it can be managed with the right approach. By focusing on healthy eating, regular exercise, and medical treatment, women with PCOS can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan and to address any concerns related to fertility, weight management, or other symptoms.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to minimizing the long-term effects of PCOS. With support and lifestyle changes, women can improve their health and manage the symptoms effectively.